AI and Machine Learning Fundamentals
AI and Machine Learning Fundamentals: An In-Depth Introduction
AI and Machine Learning (ML) have become some of the most transformative technologies of the 21st century. They power everything from voice assistants and recommendation algorithms to cutting-edge healthcare tools and autonomous vehicles. But while the impact of AI and ML is evident, understanding the underlying concepts can feel daunting for newcomers.
In this blog, we’ll break down the fundamentals of AI and Machine Learning, explaining the core concepts and techniques, including supervised and unsupervised learning, neural networks, and deep learning. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of these technologies and how they’re shaping the future.
What Are AI and Machine Learning?
Before diving into the details, let’s clarify the distinction between AI and ML:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the broad field of creating machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making. It’s an umbrella term that includes various techniques and approaches.
- Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that focuses on enabling machines to learn from data. Instead of being explicitly programmed with rules, ML models identify patterns in data to make predictions or decisions.
Example: When you use a music streaming platform, ML algorithms analyze your listening history to suggest songs you might like. This is AI in action, with ML as the specific technique driving the recommendations.
Core Concepts in Machine Learning
1. Data: The Foundation of Machine Learning
Machine learning relies on data. Whether it’s numbers, text, images, or audio, data serves as the input that helps models learn. The quality and quantity of this data directly affect a model's performance.
- Training Data: Used to teach the model by exposing it to examples.
- Testing Data: A separate dataset to evaluate the model's accuracy and reliability.
- Validation Data: Fine-tunes the model during training to avoid overfitting (more on that later).
2. Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning can be categorized into three main types based on how models learn from data:
Supervised Learning
In supervised learning, the model is trained on a labeled dataset, meaning each input comes with a corresponding output. The goal is for the model to learn the relationship between inputs (features) and outputs (labels) so it can make accurate predictions on new data.
Examples:
- Predicting house prices based on features like size, location, and number of rooms.
- Classifying emails as spam or not spam.
Techniques:
- Regression: Used for continuous outputs (e.g., predicting stock prices).
- Classification: Used for discrete outputs (e.g., identifying cats vs. dogs in images).
Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning, the model works with unlabeled data, meaning there are no predefined outputs. Instead, the model tries to identify patterns, structures, or groupings within the data.
Examples:
- Grouping customers with similar buying habits for marketing campaigns.
- Detecting anomalies in network traffic to identify potential cybersecurity threats.
Techniques:
- Clustering: Groups similar data points together (e.g., K-Means, DBSCAN).
- Dimensionality Reduction: Simplifies datasets by reducing the number of features while retaining essential information (e.g., Principal Component Analysis, or PCA).
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning involves training a model to make decisions by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. It’s often used in robotics, gaming, and autonomous systems.
Examples:
- Teaching a robot to navigate a maze.
- Optimizing energy consumption in smart grids.
Key Concepts:
- Agent: The model or algorithm making decisions.
- Environment: The context in which the agent operates.
- Reward: Feedback given to the agent for its actions.

Neural Networks: The Building Blocks of Deep Learning
Neural networks are the foundation of many modern AI systems. Inspired by the structure of the human brain, they consist of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process and transform data.
How Neural Networks Work
- Input Layer: Takes raw data, such as pixel values in an image or numerical features in a dataset.
- Hidden Layers: Process the data using mathematical operations (weights and biases) to identify patterns.
- Output Layer: Produces the final result, such as a prediction or classification.
Key Features of Neural Networks
- Activation Functions: Determine the output of a neuron (e.g., sigmoid, ReLU).
- Backpropagation: A technique used to adjust weights during training to minimize errors.
- Training: Involves iteratively feeding data through the network and adjusting parameters to improve accuracy.
Deep Learning: Taking Neural Networks Further
Deep learning is a specialized subset of machine learning that uses large neural networks with multiple layers, hence the term "deep." It excels at handling unstructured data, such as images, audio, and text.
Applications of Deep Learning
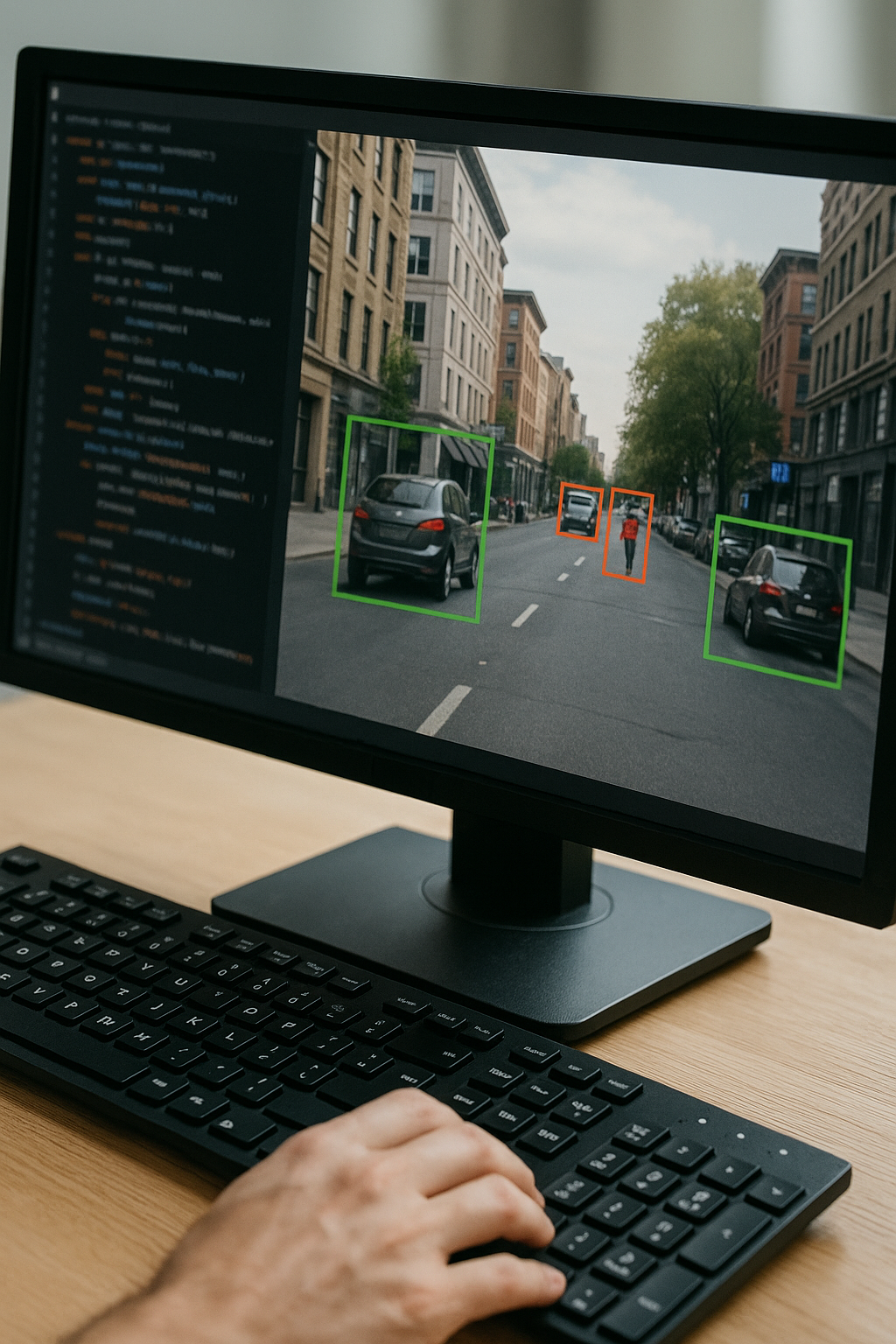
Computer Vision:
- Facial recognition.
- Object detection in autonomous vehicles.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- Machine translation (e.g., Google Translate).
- Sentiment analysis (e.g., detecting positive or negative reviews).
Healthcare:
- Diagnosing diseases from medical images.
- Predicting patient outcomes using electronic health records.
Key Techniques in Machine Learning
Training and Testing
- Training Data: Used to teach the model.
- Testing Data: Evaluates the model's performance on unseen data.
Cross-Validation
- Splits data into multiple subsets to ensure the model performs well across different samples.
Overfitting vs. Underfitting
- Overfitting: The model learns the training data too well, failing to generalize to new data.
- Underfitting: The model fails to capture patterns in the training data, resulting in poor performance.
Hyperparameter Tuning
- Adjusting model parameters, such as learning rate and number of layers, to optimize performance.
Challenges in Machine Learning
Data Quality:
- Models are only as good as the data they’re trained on. Incomplete, biased, or noisy data can lead to poor predictions.
Ethical Concerns:
- Bias in AI systems can perpetuate social inequalities.
- Transparency and accountability are critical as AI decisions impact real lives.
Computational Power:
- Training large models requires significant computational resources, limiting accessibility for smaller organizations.
Why Machine Learning Matters
Machine learning isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a transformative force across industries:
- Healthcare: Early disease detection and personalized treatment.
- Finance: Fraud detection and algorithmic trading.
- Retail: Personalized shopping experiences and inventory optimization.
- Entertainment: Content recommendations on platforms like Netflix and Spotify.
The Future of Machine Learning
As machine learning evolves, we can expect advancements in:
- Reinforcement Learning: Smarter AI agents for complex decision-making.
- Explainable AI: Making model decisions more transparent.
- Federated Learning: Training models across decentralized data while preserving privacy.
Start Your AI Journey Today
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a business leader, or a student, understanding the fundamentals of AI and machine learning is the first step toward harnessing their potential. These technologies are shaping the future—don’t get left behind.
Stay Ahead of the Curve
Want to dive deeper into AI and machine learning? Sign up for our newsletter to get exclusive insights, practical tutorials, and the latest news delivered straight to your inbox. Join our growing community and be part of the AI revolution—subscribe now!
Sign Up For Our Weekly Newsletter and Get Your FREE Ebook " AI For Everyone - Learn the Basics and Embrace the Future"